Disc Bulge vs. Herniated Disc
Share

A disc bulge and a herniated disc are two distinct conditions affecting the intervertebral discs in the spine, often confused due to their similar symptoms but differing significantly in their underlying pathology and severity.
Disc Bulge
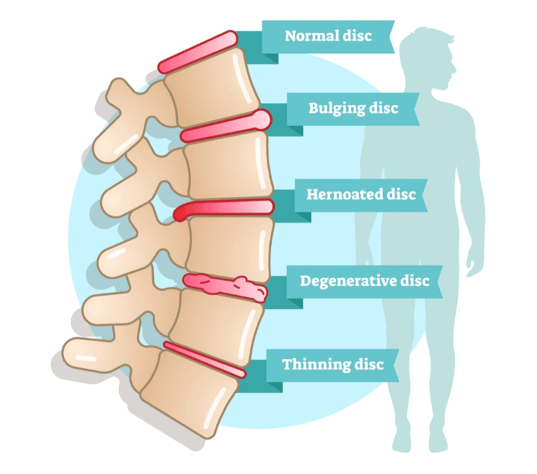
Definition: A disc bulge occurs when the outer layer of the intervertebral disc, known as the annulus fibrosus, weakens and extends outward. However, the inner gel-like core, called the nucleus pulposus, remains contained within the disc.
Appearance: The disc extends beyond its normal perimeter but retains its overall shape, resembling a slight protrusion or ballooning.
Symptoms: Often, disc bulges are asymptomatic or cause mild to moderate pain and discomfort. When symptoms do occur, they may include localized back pain or stiffness, particularly if the bulge compresses nearby structures.
Causes: Commonly due to age-related degeneration, repetitive stress, or minor trauma. Prolonged poor posture and lack of exercise can also contribute.
Treatment: Typically managed with conservative approaches such as physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, exercise, and lifestyle modifications

Herniated Disc
Definition: A herniated disc, also known as a slipped or ruptured disc, happens when the annulus fibrosus tears or ruptures, allowing the nucleus pulposus to leak out. This extrusion can compress spinal nerves or the spinal cord.
Appearance: The disc's inner material breaches the outer layer, creating a more pronounced and often irregular projection.
Symptoms: Herniated discs often cause more severe and acute symptoms compared to bulges. These can include intense pain, numbness, tingling, or weakness in the arms or legs, depending on the location of the herniation. Sciatica is a common symptom if the herniation occurs in the lower back.
Causes: Often results from acute injury, heavy lifting, sudden twisting movements, or significant degenerative changes in the spine.
Treatment: While initial treatment may still be conservative, including rest, physical therapy, and medications, more severe cases may require interventions such as epidural steroid injections or surgical procedures like discectomy.

Key Differences
Severity and Symptomatology: Disc bulges typically cause milder symptoms and are less likely to compress nerves severely. Herniated discs often result in significant nerve compression and more severe pain and neurological deficits.
Structural Integrity: In a bulge, the disc's outer layer remains intact, whereas, in a herniation, the inner core breaches this layer.
Treatment Approaches: Bulges usually respond well to non-surgical treatments, while herniations, especially those causing significant symptoms, may necessitate surgical intervention.
Understanding these differences is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment planning, ensuring patients receive appropriate care tailored to their specific condition.