PCOS and their symptoms.
Share
What is PCOS?
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common endocrine disorder that affects women of reproductive age. It is characterized by hormonal imbalances, irregular menstrual cycles, and the presence of multiple small cysts on the ovaries. PCOS is a complex condition with a variety of symptoms and can lead to complications such as infertility, metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease.
Common Symptoms of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
-
Irregular Periods:
- Infrequent, irregular, or prolonged menstrual cycles are common. Some women with PCOS may have fewer than nine periods a year, and their cycles might be longer than 35 days. Some may experience very heavy bleeding during periods.
- it is caused due to hormonal imbalances, particularly elevated levels of androgens and insulin, disrupt the normal ovulatory cycle, leading to irregular or missed periods.
-
Excess Androgen Levels:
- Elevated levels of male hormones (androgens) are a hallmark of PCOS and can result in physical signs such as hirsutism (excessive hair growth on the face, chest, and back), severe acne, and male-pattern baldness (hair thinning on the scalp).
- The ovaries produce abnormally high levels of androgens, which interfere with the development and release of eggs during ovulation.
-
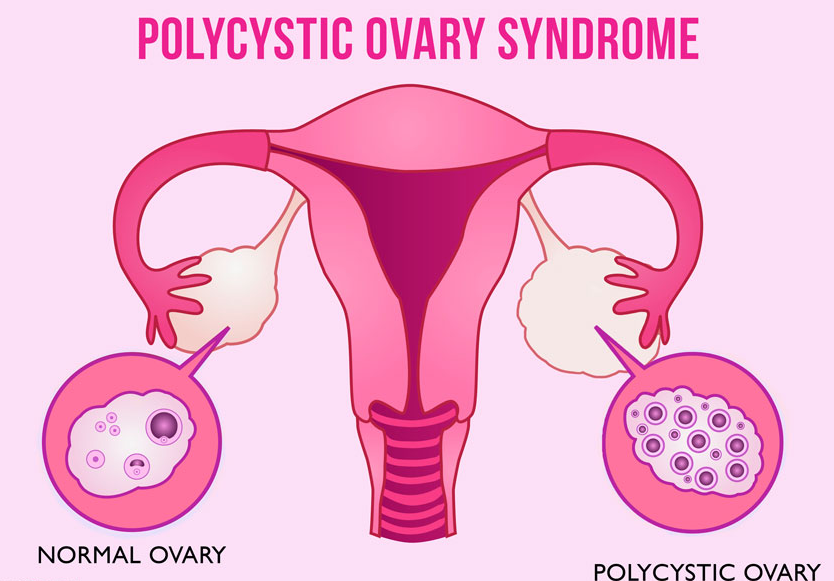
Polycystic Ovaries:
- Enlarged ovaries containing numerous small fluid-filled sacs (follicles) that surround the eggs. This can be observed via ultrasound.
- Hormonal imbalances prevent follicles from maturing and releasing eggs, resulting in the formation of multiple small cysts.
-
Weight Gain:
- Many women with PCOS are overweight or obese, and they may find it difficult to lose weight. This weight is often carried around the abdomen, contributing to an increased risk of metabolic issues.
- Insulin resistance and hormonal imbalances contribute to weight gain. High insulin levels promote fat storage and make weight loss more difficult.

-
Insulin Resistance:
- The body’s cells become less responsive to insulin, causing the pancreas to produce more insulin to compensate. Elevated insulin levels can also increase androgen production, exacerbating other PCOS symptoms like elevated blood sugar levels or an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes etc.
-
Skin Issues:
- Darkening of the skin, particularly in creases around the neck, groin, and under the breasts (a condition called acanthosis nigricans). Skin tags, which are small excess skin growths, are also more common.
- it is caused due to high insulin levels which can stimulate the growth of skin cells and the production of melanin, leading to these dark patches.

-
Infertility:
- PCOS is one of the most common causes of infertility. The hormonal imbalance can interfere with the growth and release of eggs from the ovaries (ovulation).making it difficult to conceive.

- PCOS is one of the most common causes of infertility. The hormonal imbalance can interfere with the growth and release of eggs from the ovaries (ovulation).making it difficult to conceive.
-
Mood Changes:
- The chronic nature of PCOS and the impact of hormonal imbalances can contribute to mental health issues. Additionally, insulin resistance and inflammation may play a role in mood changes, depression stress and anxiety.
-
Sleep Apnea:
- Women with PCOS, particularly those who are overweight, are at a higher risk of developing sleep apnea, a disorder characterized by repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep.
-
Pelvic Pain:
- Some women with PCOS experience pelvic pain, which can occur during their menstrual period or at other times.
-
. Thinning Hair (Androgenic Alopecia).
- Elevated levels of androgens can cause hair follicles to shrink, leading to hair thinning or loss on the scalp, often referred to as male-pattern baldness.

- Elevated levels of androgens can cause hair follicles to shrink, leading to hair thinning or loss on the scalp, often referred to as male-pattern baldness.
Management:
While there is no cure for PCOS, its symptoms can be managed through lifestyle changes and medical treatments:
- Lifestyle Modifications: By adopting a balanced diet that focuses on whole, nutrient-dense foods and avoiding processed and high-sugar items, women with PCOS can better manage their symptoms and improve their overall health.
- Yoga or Exercise : Incorporating both yoga and regular exercise into your routine can significantly improve PCOS symptoms and enhance overall health and its well-being, by managing weight and insulin levels.
- Supplements : Certain supplements can help in alleviating symptoms, improving overall health and can help in managing PCOS like Inositol, Vit D, Chromium, N-Acetyl Cysteine (NAC) , Berberine, zinc etc.
- Medications: Birth control pills to regulate periods, anti-androgens to reduce hair growth and acne, and metformin to improve insulin resistance.
- Fertility Treatments: Medications to induce ovulation or assisted reproductive technologies for those trying to conceive.
Managing PCOS often requires a multidisciplinary approach, involving gynecologists, endocrinologists, dietitians, and other healthcare professionals. Regular monitoring and adapting treatment plans as needed can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.