Gout : How does it progress?
Share

Gout is a type of arthritis that results from the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints, leading to inflammation, pain, and stiffness. Uric acid is a waste product that is produced when the body breaks down purines, which are found in many foods and also occur naturally in the body. Normally, uric acid is dissolved in the blood and excreted through the kidneys. However, in some people, the body produces too much uric acid or the kidneys do not excrete it properly, leading to high levels of uric acid in the blood. When the uric acid level is high, it can form sharp, needle-like crystals that accumulate in the joints, causing pain and inflammation.
Gout is often described as one of the most painful types of arthritis. The pain is usually sudden and severe, often starting in the middle of the night or early morning. The affected joint becomes red, swollen, and extremely tender to the touch. Even the weight of a sheet or blanket can be unbearable. The pain can be so intense that it can wake a person up from sleep and make it difficult to walk or perform daily activities.
The most commonly affected joint in gout is the big toe, but it can also occur in other joints, such as the ankle, knee, wrist, or elbow. Gout attacks can last from a few days to a few weeks, and they may occur sporadically or with increasing frequency over time. In addition to joint pain, gout can also cause fever, chills, and a general feeling of illness.
The severity of gout pain can vary depending on the individual, the affected joint, and the stage of the disease.
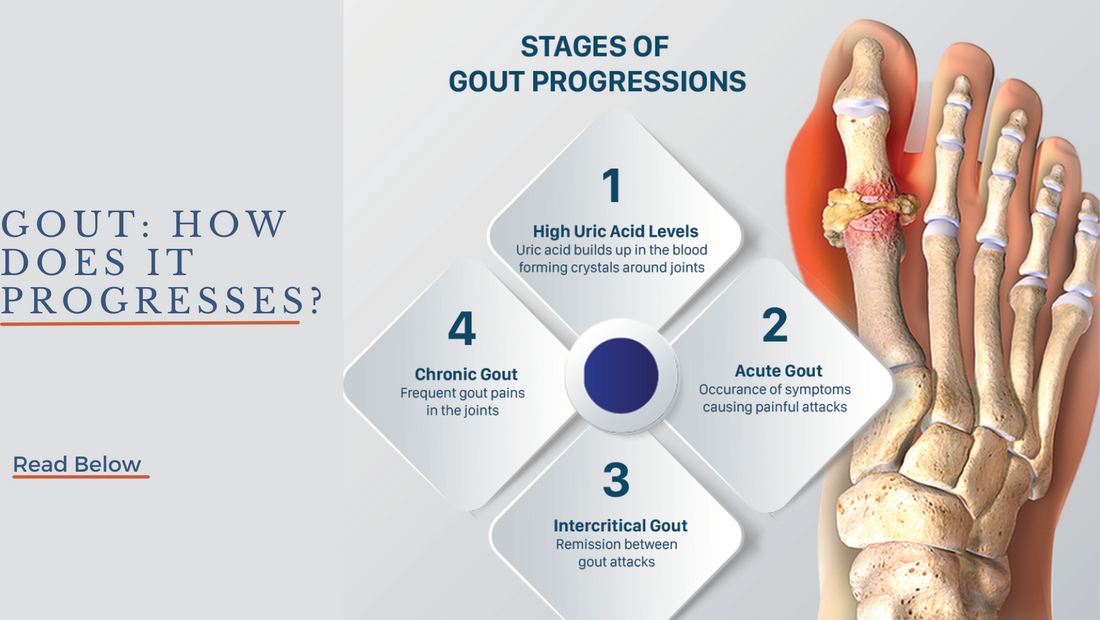
If left untreated, gout can progress through four stages, each with increasingly severe symptoms and complications. Here's what you need to know about the stages of gout.
Stage 1: Asymptomatic Hyperuricemia In the early stages of gout, there may be no noticeable symptoms. However, the uric acid levels in the blood may be higher than normal, a condition known as asymptomatic hyperuricemia. This stage can last for years, and many people with high uric acid levels never develop gout. However, it's important to monitor uric acid levels and make lifestyle changes to lower them, as high uric acid levels can lead to gout attacks in the future.
Stage 2: Acute Gout Attack The second stage of gout is marked by the first acute gout attack, which is usually sudden and severe. The pain and inflammation are most commonly felt in the big toe, but they can also occur in other joints such as the ankle, knee, or wrist. The affected joint may be red, swollen, and extremely tender to the touch. The acute gout attack can last for several days to several weeks, and it may resolve on its own or with treatment.
Stage 3: Intercritical Gout After the acute gout attack subsides, there may be a period of time without symptoms, known as intercritical gout. During this stage, there are no active gout attacks, but the risk of future attacks remains high. It's important to continue monitoring uric acid levels and making lifestyle changes to prevent future attacks.
Stage 4: Chronic Tophaceous Gout In the final stage of gout, chronic tophaceous gout, there are frequent gout attacks and the formation of tophi, or deposits of uric acid crystals, in the joints and soft tissues. The tophi can cause deformities, damage to the joints, and chronic pain. In addition, high uric acid levels can lead to the development of kidney stones and kidney damage. Treatment during this stage is focused on managing symptoms, preventing complications, and reducing the risk of future attacks.
In conclusion, gout is a progressive condition that can cause significant pain and complications if left untreated. By monitoring uric acid levels, making lifestyle changes, and seeking prompt treatment for acute gout attacks, it's possible to prevent or slow the progression of gout through its stages by taking proper supplements like The Joints Co Gout Ease. If you're experiencing symptoms of gout or have a family history of gout, talk to your doctor about monitoring your uric acid levels and developing a treatment plan.
Gout is a painful condition caused by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints. It can progress through four stages, each with increasingly severe symptoms and complications. The early stage of gout, known as asymptomatic hyperuricemia, may have no noticeable symptoms, but the uric acid levels in the blood may be higher than normal. Acute gout attacks are sudden and severe, and may occur in the big toe or other joints. After an acute gout attack subsides, there may be a period of time without symptoms, known as intercritical gout. Chronic tophaceous gout is the final stage of gout, where there are frequent gout attacks and the formation of uric acid crystals in the joints and soft tissues.
To avoid the condition from worsening, it's essential to monitor uric acid levels, make lifestyle changes, and seek prompt treatment for acute gout attacks. Lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight, limiting alcohol intake, ,avoiding foods high in purines and timely prevention through supplements like The Joints Co Gout Ease may help reduce the risk of future attacks. If you're experiencing symptoms of gout or have a family history of gout, it's essential to talk to your doctor about monitoring your uric acid levels and developing a treatment plan. By taking steps to prevent or slow the progression of gout, it's possible to manage the condition and improve quality of life.